| CAS: | 61-54-1 |
| MF: | C10H12N2 |
| MW: | 160.22 |
| EINECS: | 692-120-0 |
| Product Categories: | Non-Chiral heterocyclic compounds;Indole;Indoles;Tryptamines;Amines;Heterocycles;Drug Intermediates;Inhibitors;1;61-54-1;API |
| Mol File: | 61-54-1.mol |
| Tryptamine Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 113-116 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 137 °C/0.15 mmHg (lit.) |
| density | 0.9787 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6210 (estimate) |
| Fp | 185 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | water: soluble1g/L at 20°C |
| pka | 10.2(at 25℃) |
| form | crystalline |
| color | white |
| PH | 11.07 (10g/l, H2O, 24.7℃) |
| Water Solubility | negligible |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,9796 |
| BRN | 125513 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 61-54-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1H-Indole-3-ethanamine(61-54-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tryptamine (61-54-1) |
| reparation | Tryptamine, a monoamine alkaloid containing an indole ring structure is derived by the decarboxylation of amino acid tryptophan.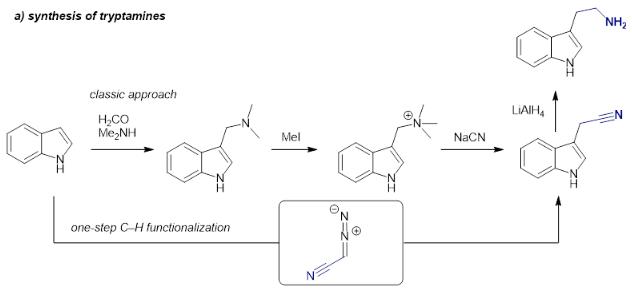 The synthesis of tryptamines is typically conducted following a classic route starting with a Mannich reaction of an indole heterocycle, followed by quaternization of the amine, nucleophilic substitution with highly toxic cyanide and final reduction. |
| General Description | Tryptamines which are usually found in plants, fungi, animals, etc. are categorized under the monoamine alkaloids class of compounds. |
| Biochem/physiol Actions | Vasoactive; may have a neuromodulator function; biogenic amine formed from the decarboxylation of tryptophan by L-aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. |
| Purification Methods | Crystallise tryptamine from *benzene, Et2O (m 114o) or pet ether (m 118o). It has UV: 222n 276, 282 and 291nm (EtOH) and max 226, 275, 281 and 290nm (HCl). [Beilstein 22 II 346, 22 III/IV 4319, 22/10 V 45.] |





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.